Surveillance Cameras
- Home
- Night vision and thermal cameras
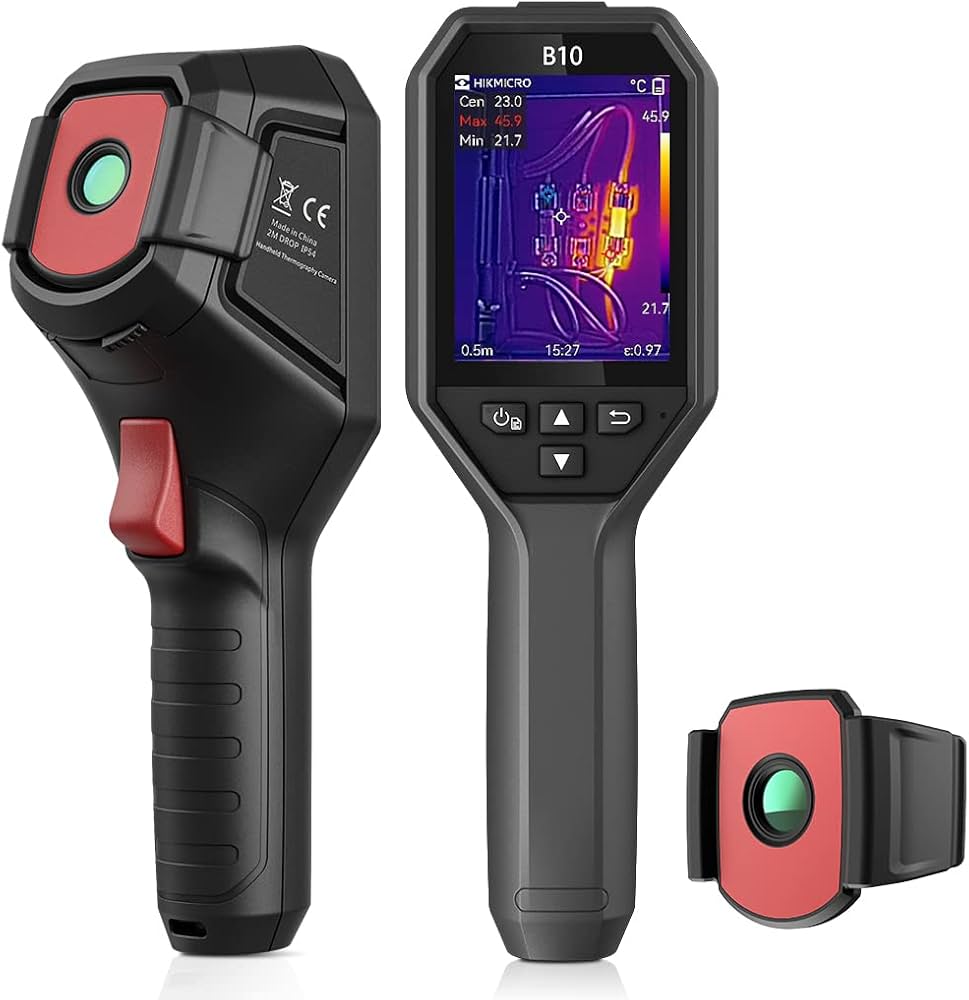

Night vision and thermal cameras
Night Vision and Thermal Cameras are both technologies used to see in low-light or no-light conditions, but they operate very differently. Here’s a comparison to help you understand:
Night Vision Cameras
How They Work:
- Amplify available light (like moonlight, starlight, or infrared light).
- Use image intensifiers to enhance visibility in the dark.
Features:
- You see a greenish image (common due to how human eyes perceive green better in low light).
- Best when some light is present.
- Cannot see through fog, smoke, or walls.
- Often used in military, security, wildlife observation.
Types:
- Analog Night Vision (Gen 1, Gen 2, Gen 3): Traditional military-style tubes.
- Digital Night Vision: Uses sensors and displays, often cheaper and more versatile.
Thermal Cameras
How They Work:
- Detect heat (infrared radiation) emitted by all objects.
- Create an image based on temperature differences.
Features:
- Work in complete darkness, fog, smoke, or foliage.
- Show images in black/white or color gradients (hot = white/red/yellow, cold = black/blue).
- Can detect hidden objects (e.g., warm body behind bushes).
- Widely used in search & rescue, firefighting, electrical inspections, security.
Types:
- Cooled Thermal Cameras: Higher sensitivity, longer ranges, expensive.
- Uncooled Thermal Cameras: More common and affordable.